AI interpretation of intracranial hemorrhage
Research & Innovation
AI interpretation of intracranial hemorrhage
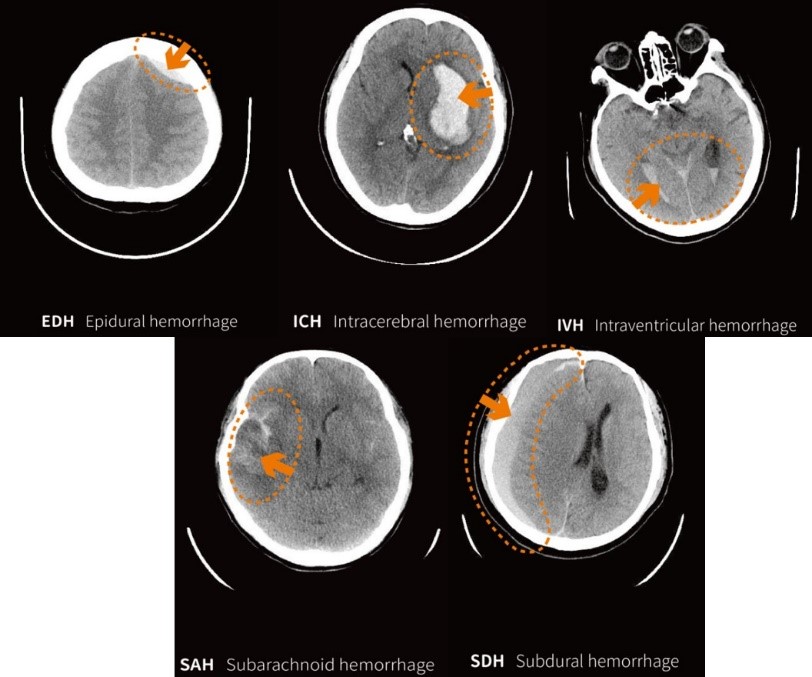
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) occurs in 24 out of every 100,000 people every year, and the mortality rate is as high as 30%, making it a critical emergency. According to the current situation of emergency department in Taiwan, the fatality rate of patients with brain injury is high, and it may even lead to sequelae of stroke.
To diagnose for a patient and determine whether there are symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage, physicians usually need to interpret a large number of brain computed tomography (CT) images for diagnosis and follow-up medical decisions. In order to grasp the prime time to treat patients and speed up the communication in the hospital referral process, this project uses CT images without contrast agent as the training set to establish a model that can accurately identify five types of intracranial hemorrhage (EDH / SDH / SAH / ICH / IVH), which can quickly notify medical care, reduce patients’ waiting time, and allow them to receive proper treatment immediately. The accuracy rate of interpreting image of brain hemorrhage has reached 98.6%.