Intelligent Brain Rescue System (iBRS)
Research & Innovation
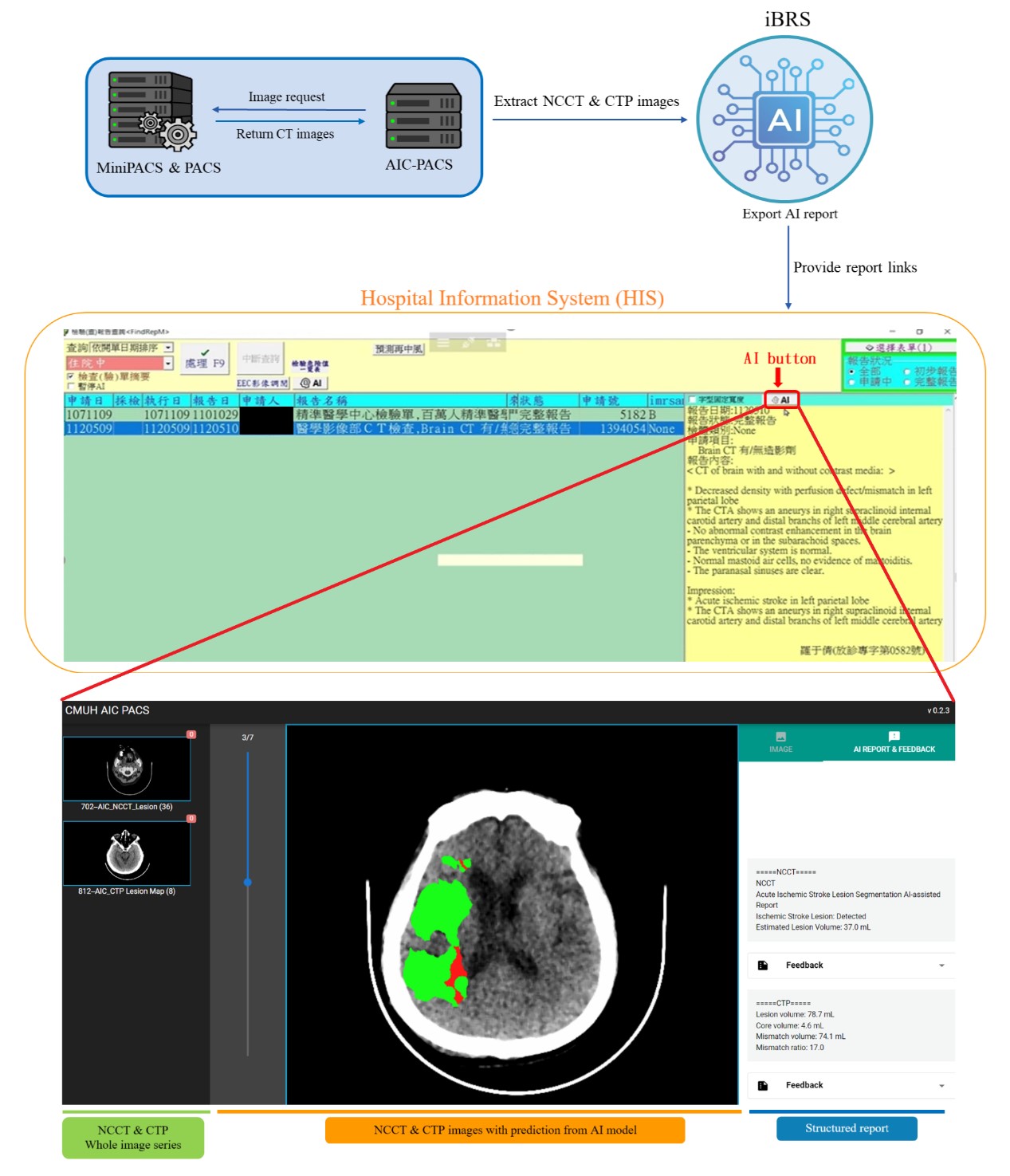
Intelligent Brain Rescue System (iBRS)
After a stroke occurs, it can seriously affect a patient's physiological functions, and may even lead to death. Computer tomography (CT) examination is a very important advanced medical imaging diagnostic technique nowadays. For the diagnosis of ischemic stroke, clinical diagnosis of ischemic stroke and assessment of its extent based on brain flow scans (CT perfusion, CTP), it takes additional time (about 15 to 30 minutes) to inject the contrast agent and complete the brain scan, which may delay the patient's urgent thrombolysis treatment. In addition, if the patient cannot undergo a CTP examination due to physiological factors, the doctor can only rely on a small amount of information to make medical decisions, which invisibly increases the uncertainty of diagnosis.
In short, the biggest clinical highlight of this case is that using the model trained by non-contrast CT (NCCT), the doctor can quickly diagnose large vessel occlusion (LVO) without the need for contrast agent injection. Compared with traditional diagnosis of ischemic stroke, it can save about 30 minutes of additional CTP examination time and obtain detailed AI interpretation results. In addition, hospitals without CTP equipment can also benefit. Through the interpretation results of this system, the time for transferring patients to a large hospital can be significantly reduced (about several hours).
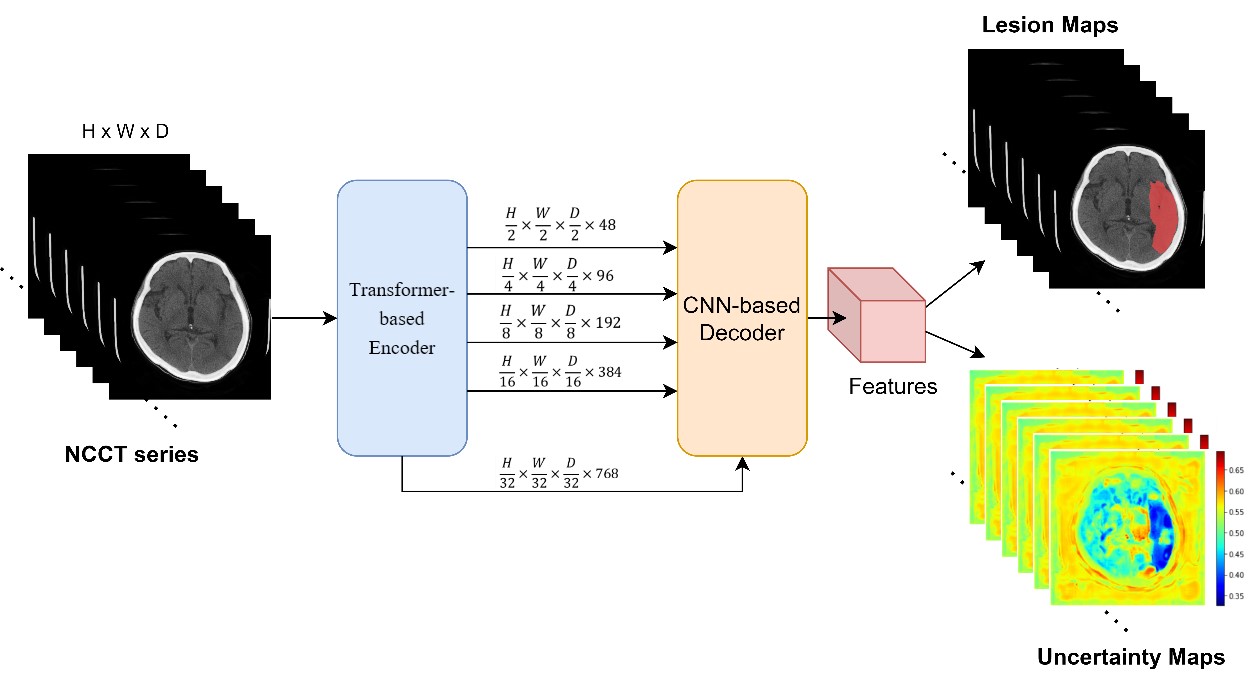
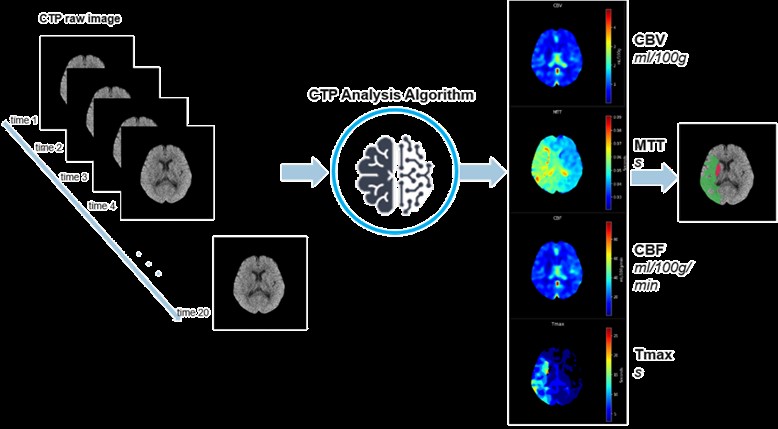
Our center uses data from nearly 400 patients to construct an artificial intelligence model- "Ischemic Stroke Detection System under Non-contrast CT (NCCT)", which analyzes NCCT images and simulates the image after injecting contrast agent to predict the brain region affected by the patient's damage. By integrating clinical information, it can diagnose whether there is an acute ischemic stroke and combine with the subsequent "Brain Flow Scan (CTP) Imaging Intelligent Analysis System" to analyze the judgment of the stroke position and its extent obtained by AI from CTP. This includes the ischemic area of the brain, its core area (ischemic core), and the ischemic penumbra area, to confirm the information such as the treatable area and untreatable area, and to assist doctors in judging the effectiveness of their treatment.