Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
Exercise ECG - Coronary Artery Disease AI-Assisted Detection System
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a cardiovascular disease caused by narrowing or blockage of the arteries. Patients may initially experience warning signs such as chest tightness, shortness of breath, and dizziness. If not discovered and treated promptly, it can lead to a series of serious complications, including heart failure, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, and even sudden death. An exercise electrocardiogram (Exercise ECG) is one of the most commonly used clinical examinations for diagnosing coronary artery disease. Patients undergo ECG testing under exercise stress to evaluate whether myocardial hypoxia exists, thereby inferring whether the patient has coronary artery disease and assessing their risk. During interpretation, physicians must simultaneously integrate changes from multiple twelve-lead ECGs, patient symptoms, and physiological indicators during multiple examinations to make accurate judgments and risk assessments. This not only highly depends on the physician's clinical experience but is also limited by subjective factors and differences in interpretation difficulty. Combined with physicians' busy clinical work, they often cannot complete interpretations promptly, affecting diagnostic efficiency and treatment timing.
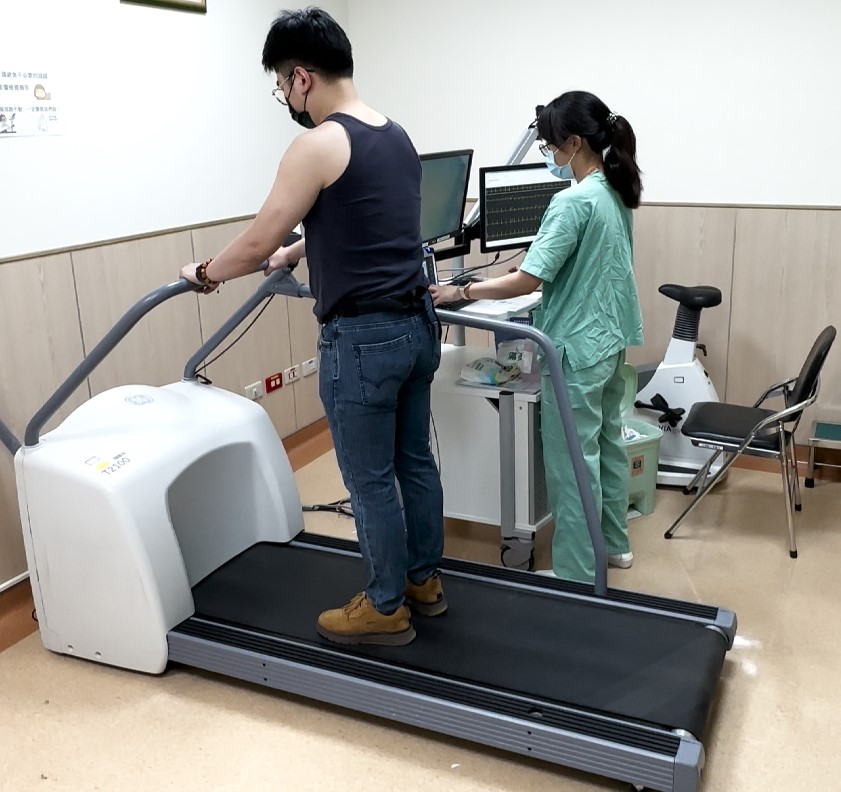

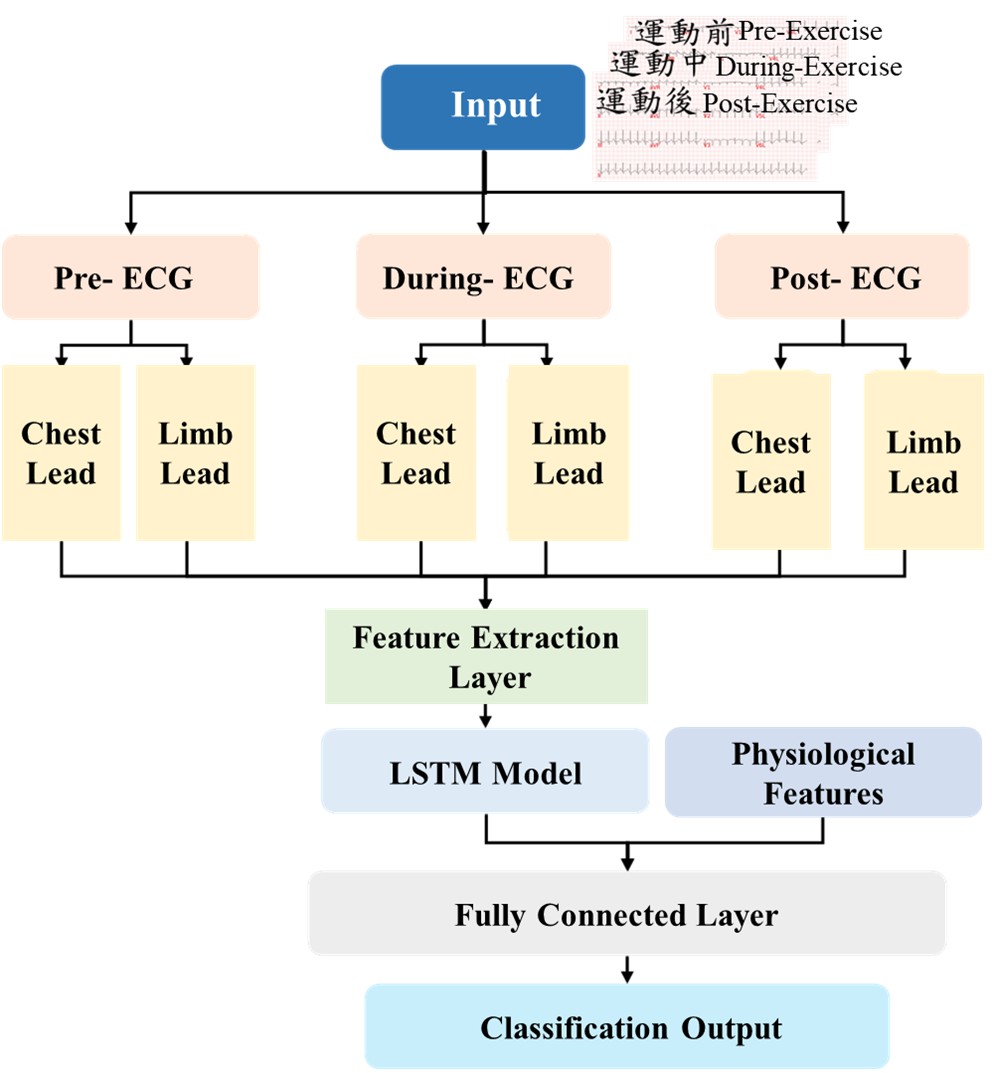
To solve these problems, our hospital's Artificial Intelligence Center and Cardiovascular System team collaborated to break through traditional diagnostic limitations using deep learning technology for patient exercise. They successfully developed the "Exercise ECG - Coronary Artery Disease AI-Assisted Detection System." This system innovatively integrates ECG signals from three time points—before, during, and after exercise—combined with other physiological features to quickly determine whether coronary arteries are severely narrowed (>70%).
The system not only demonstrates impressive effectiveness (80% accuracy, 88% sensitivity) but also significantly improves diagnostic efficiency! Physicians can receive real-time AI second expert opinions to make more precise diagnoses; operators can also identify high-risk patients earlier, reducing interpretation time from the traditional 7-30 days to 1-3 days, promptly reminding patients to return for follow-up visits sooner, allowing them to receive appropriate treatment faster. From May 17, 2022, to April 15, 2025, this system has assisted in interpreting 21,563 exercise ECG examinations.
Awards
2023
- National Healthcare Quality Award (NHQA)
- Symbol of National Quality (SNQ)
- National Innovation Award
Patents
- Certified Taiwan Patent (Certificate No. I856824)
Contact window
Project Management Group
Phone:+886-4-22052121 ext 12534
