Digital Imaging and Virtualization
Fundus Image Detection for Diabetic Retinopathy
According to statistics from the National Health Research Institute's "2019 Taiwan Diabetes Yearbook," the prevalence of diabetes in Taiwan exceeds 9.32%, with more than 2.2 million diabetic patients. Among these, diabetes can lead to various vascular complications and is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults. Therefore, diabetic patients should undergo fundus photography examination at least once a year to prevent vision impairment caused by severe diabetic retinopathy.
With the increasing number of diabetic patients and insufficient accessibility to screening, patients cannot be referred to ophthalmology specialists for timely treatment at the earliest opportunity. To make clinical operations more efficient (helping front-line physicians in family medicine, endocrinology, internal medicine, etc. diagnose diabetic retinopathy) and reduce the risk of blindness in patients, our hospital's Artificial Intelligence Center collaborated with a professional ophthalmology team to develop a Diabetic Retinopathy Assisted Diagnosis and Grading System, categorizing into 3 levels according to lesion severity.
System performance: AUC (Area Under ROC Curve) 0.986 (Grade 0), 0.902 (Grade 1), 0.952 (Grade 2). In addition to diabetes, our hospital is also actively developing other fundus lesion-assisted interpretation, such as for glaucoma.
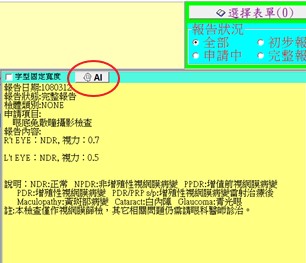
_03.jpg)
The application of this system has extended to remote consultations in Dili Village, Xinyi Township, Nantou County.Diabetic patients can undergo fundus examinations in the clinic, with the AI system interpretation providing recommendations to physicians.Ophthalmologists at China Medical University Hospital can simultaneously see the patient's examination images and reports in real-time, diagnosing whether there are abnormalities in the optic disc.The combination of AI and telemedicine implements localized healthcare, providing medical center-level services to patients in remote areas.
Awards
2019
- NHQA National Healthcare Quality Award
Contact window
Project Management Group +886-4-22052121 ext.12534
